Hello friends today we are going to see the structure of C programming language which we are used as a computer language. How to write a C program? where is 'C' stands for? if you want to see video tutorial of this post please see the following link. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m68iNchCRcA
The answer of above question is- 'C' is a middle level language which means we have already seen when computers were first developed, the only way they could be programmed was in terms of binary numbers, which corresponded directly to specific machine instructions.
The next technological software occurred in the development of assembly language with the help of mnemonics to perform various operations. A special program, known as an assembler, translates the assembly language program into its specific machine instructions of the computer system. The programmer must learn the instruction set of particular computer system in order to write a program and resulting program is not portable i.e. the program will not run on a different computer model. This is because different computer systems have different instructions sets, and they are all machine dependent.
Then along came so called higher level languages FORTran, BASIC, COBOL etc. These languages have been designed to give a better programming efficiency.
'C' stands in between two categories. That's why it is often called a middle level language- A relatively good programming efficiency as compared to machine oriented language and a relatively good machine efficiency as compared to high level language.
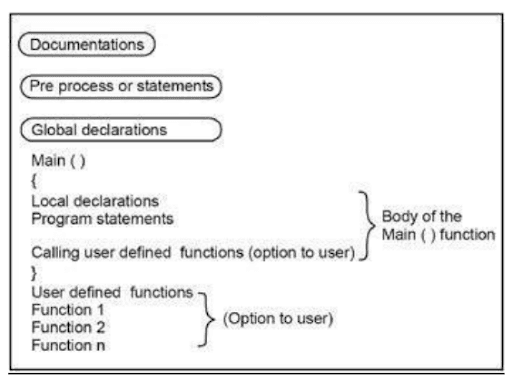
Structure of 'C' Program
Above figure shows the structure of C language, each part we will see one by one.
Documentation Section
It consists of a set of comment lines giving the names of the program, the author name and other details which the programmer would like to use later to link another program.
Preprocessor
The 'C' preprocessor provides the tools that enable to programmer to develop programs that are easier to develop, easier to read, easier to modify and easier to transport to a different computer system.
The preprocessor is a part of the C compilation process that recognizes special statements, analyzes these statements before analysis of the actual program. It is identified by the sign '#' which must be the first character on the line.
example: #define TRUE 1 : defines the name TRUE and makes it equivalent to the constant value 1.
# include "Math.h" : The preprocessor enables to collect all of your definitions into a separate file and then include them in your program.
Global declarations
There are some variables that are used in more than one functions such variables are called global variables and these variables are declared in the global declaration section. These section also declares all the user defined functions.
Main() function
Every'C' program must have one main() function to indicates main program actually starts. This function begins the opening brass { and closing with closing brass } resp. In between the opening and closing brasses we arr keeping different types of statements such as variable declaration statements, normal arithmetic statements or decision making and subroutine statements etc. Every simple statement ends with semicolon(;).
Subroutine Section
The subroutine section defines all the user defined functions which user have written for their own purpose means small program which is easy to execute, easy to modify, easy to store and easy to called any where as per their requirement.
After creating small user defined program, main function is calling that program to execute.
example:
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int a, int b)
{
int c=a+b;
return c;
}
int main(
{
int var1 =10;
int var2 = 20;
int var3 = sum(var1, var2);
printf("%d", var3);
return 0;
}In above example, we can see the subroutine program and main program.
How you found this post? is it useful? please feel free to give the comments. If you want video tutorial of this post please click here Subscribed to the My Computer Tutors for updates. I will keep updating to you with latest tutorials.